ON GRID
OVERVIEW
An On-Grid Solar Photovoltaic System, also known as a Grid-Tied System, is a solar power generation system which is connected to the Utility Grid, which is operated by the Distribution company supplying electricity to your location.
An On-Grid Solar PV system does not store electricity locally. Power generated by the Solar PV Panels Solar PV Panels convert the energy from the sun’s rays into electricity in the form of a Direct
Current (DC).
Arrays of Solar PV Panels are connected in a combination which ensures maximum
power output.
is used against the load applied (local energy consumption). Excess power that is generated is supplied to
the Utility Grid.
Similarly, when the Power generated by the Solar PV system is not enough to satisfy the requirement of
the load applied, Power is imported from the Utility Grid.
Solar generation can occur any time from 7:00 am to 6:00pm depending on the orientation of the system, the weather and other factors but peak generation usually occurs between 10:00am and 2:00pm.
The difference in units of Power imported and exported is calculated with the help of a Bi-directional meter (Net meter) A bi-directional meter, also known as a net meter, is used to indicate the net power imported or
exported.
As opposed to a traditional uni-directional meter which only indicates the power
imported by the system from the Utility Grid, a bi-directional meter indicates three readings; the
power imported from the grid, the power exported to the grid and the net power difference
between the two. and this reading is used for billing purposes by your Utility company.
HOW IT WORKS
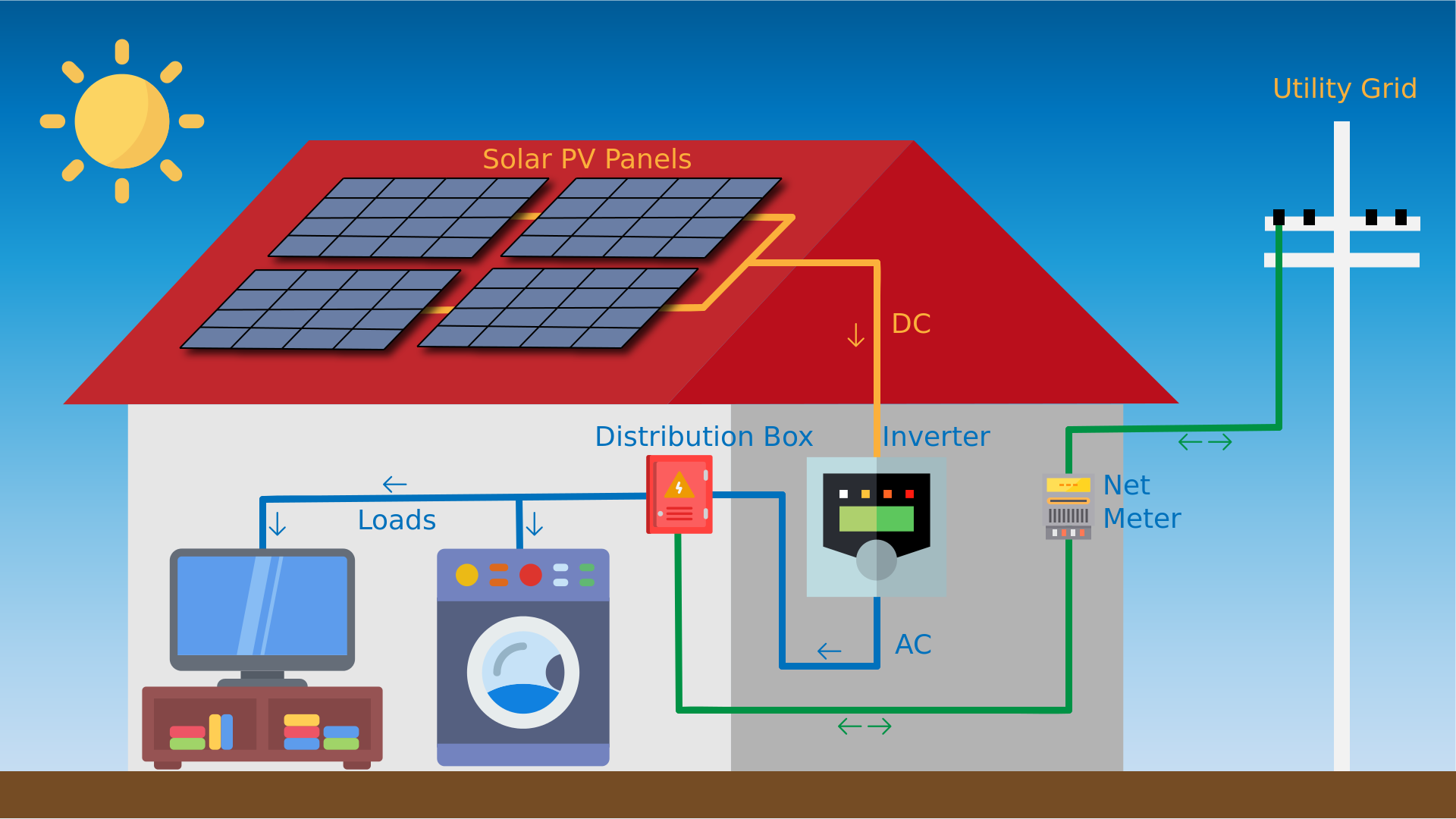 Sunlight falling on the Solar PV Panels generates a DC current in the system.
The combined power resulting from the current in the Solar arrays is fed to the Inverter which converts the DC power into grid compatible AC power.
A distribution box connects the power from the Inverter and the Utility Grid to the load.
The load draws power from the Solar PV Panels via the Inverter or from the Utility Grid
depending on the Solar PV Panel generation.
Sunlight falling on the Solar PV Panels generates a DC current in the system.
The combined power resulting from the current in the Solar arrays is fed to the Inverter which converts the DC power into grid compatible AC power.
A distribution box connects the power from the Inverter and the Utility Grid to the load.
The load draws power from the Solar PV Panels via the Inverter or from the Utility Grid
depending on the Solar PV Panel generation.
Solar PV Panels
Inverter
Distribution Box
Load
Solar PV Panels
Solar PV Panels convert the energy from the sun’s rays into electricity in the form of a Direct Current (DC).
Arrays of Solar PV Panels are connected in a combination which ensures maximum power output.
Inverter
An Inverter converts the Direct Current (DC) received from the Solar PV Panels and converts it into grid compatible Alternating Current (AC).
The number and capacity of Inverters used in a Solar PV System depends upon the local environment and the layout of the Solar PV Panels.
Bi-directional Meter
A bi-directional meter, also known as a net meter, is used to indicate the net power imported or exported.
As opposed to a traditional uni-directional meter which only indicates the power imported by the system from the Utility Grid, a bi-directional meter indicates three readings; the power imported from the grid, the power exported to the grid and the net power difference between the two.
ADVANTAGES
OF AN
ON-GRID SYSTEM
Guaranteed savings on your electricity bill
The power generated by an On-Grid Solar PV System is guaranteed to be cheaper than the power imported from the Utility Grid
The ‘buy back period’ for a Solar PV System is generally less than 5 years, meaning you can recover your investment in less than 5 years
No batteries needed
An On-Grid Solar PV System does not require having local storage of power
This eliminates a need for batteries, which brings the cost of the system down
It also saves the owner of the Solar PV System from maintaining and storing the batteries, thus saving on space